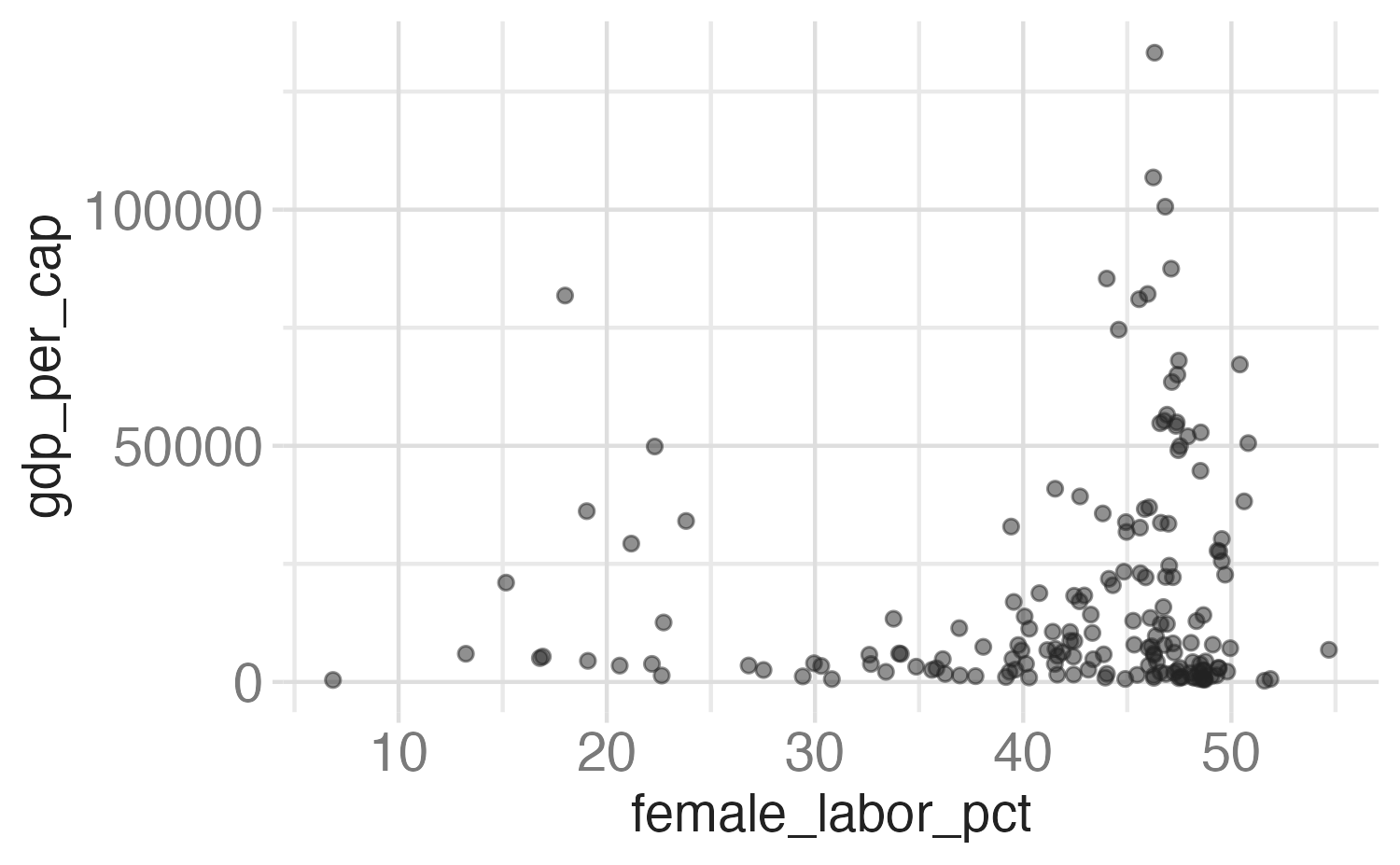
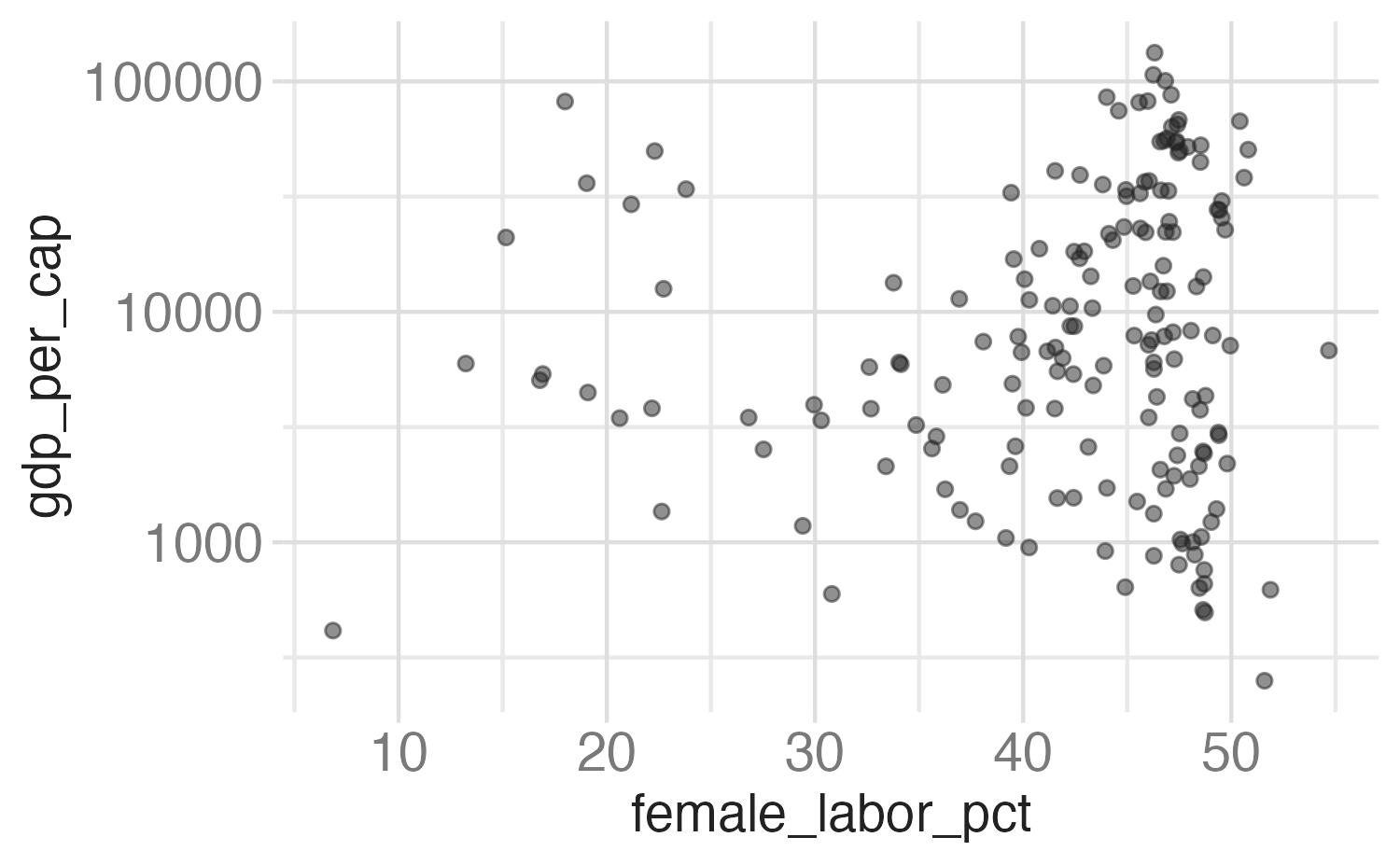
# A tibble: 174 × 8
iso2c country year gdp_per_cap female_labor_pct life_exp pop income_level
<chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <fct>
1 AF Afghanistan 2023 414. 6.85 66.0 41454761 Low income
2 AO Angola 2023 2916. 49.4 64.6 36749906 Lower middle inc…
3 AL Albania 2023 9731. 46.4 79.6 2414095 Upper middle inc…
4 AE United Arab Emirates 2023 49851. 22.3 82.9 10483751 High income
5 AR Argentina 2023 14262. 43.2 77.4 45538401 Upper middle inc…
6 AM Armenia 2023 8159. 47.2 77.5 2964300 Upper middle inc…
7 AU Australia 2023 65058. 47.4 83.1 26659922 High income
8 AT Austria 2023 56580. 46.9 81.5 9131761 High income
9 AZ Azerbaijan 2023 7133. 49.9 74.4 10153958 Upper middle inc…
10 BI Burundi 2023 251. 51.6 63.7 13689450 Low income
# ℹ 164 more rowsDeep dive: stats + scales + guides
Lecture 5
Cornell University
INFO 3312/5312 - Spring 2026
February 3, 2026
Announcements
Announcements
- Waitlist update
- 15 pins distributed so far
- INFO 3312: 0 seats available and 10 on the waitlist (4 IS majors)
- INFO 5312: 2 seats available and 0 on the waitlist
- Must use PIN by 11:59pm tonight
- Homework 02 due tomorrow
- Project 01
Project 01
- Project description
- Team assignments on Thursday
- Deliverables
- Complete team preference survey
Source: @LinkedInLunat1c
Learning objectives
- Define the statistical adjustment and scales components of the grammar of graphics
- Demonstrate how to use
stat_*()functions from {ggplot2} - Implement scale transformations for \(x\) and \(y\) axes
- Modify guides to change the visual appearance of scales on plots
Setup
World Bank indicators
Stats
Stats < > geoms
- Statistical transformation (stat) transforms the data, typically by summarizing
- Many of {ggplot2}’s stats are used behind the scenes to generate many important geoms
stat |
geom |
|---|---|
stat_bin() |
geom_bar(), geom_freqpoly(), geom_histogram() |
stat_bin2d() |
geom_bin2d() |
stat_bindot() |
geom_dotplot() |
stat_binhex() |
geom_hex() |
stat_boxplot() |
geom_boxplot() |
stat_contour() |
geom_contour() |
stat_quantile() |
geom_quantile() |
stat_smooth() |
geom_smooth() |
stat_sum() |
geom_count() |
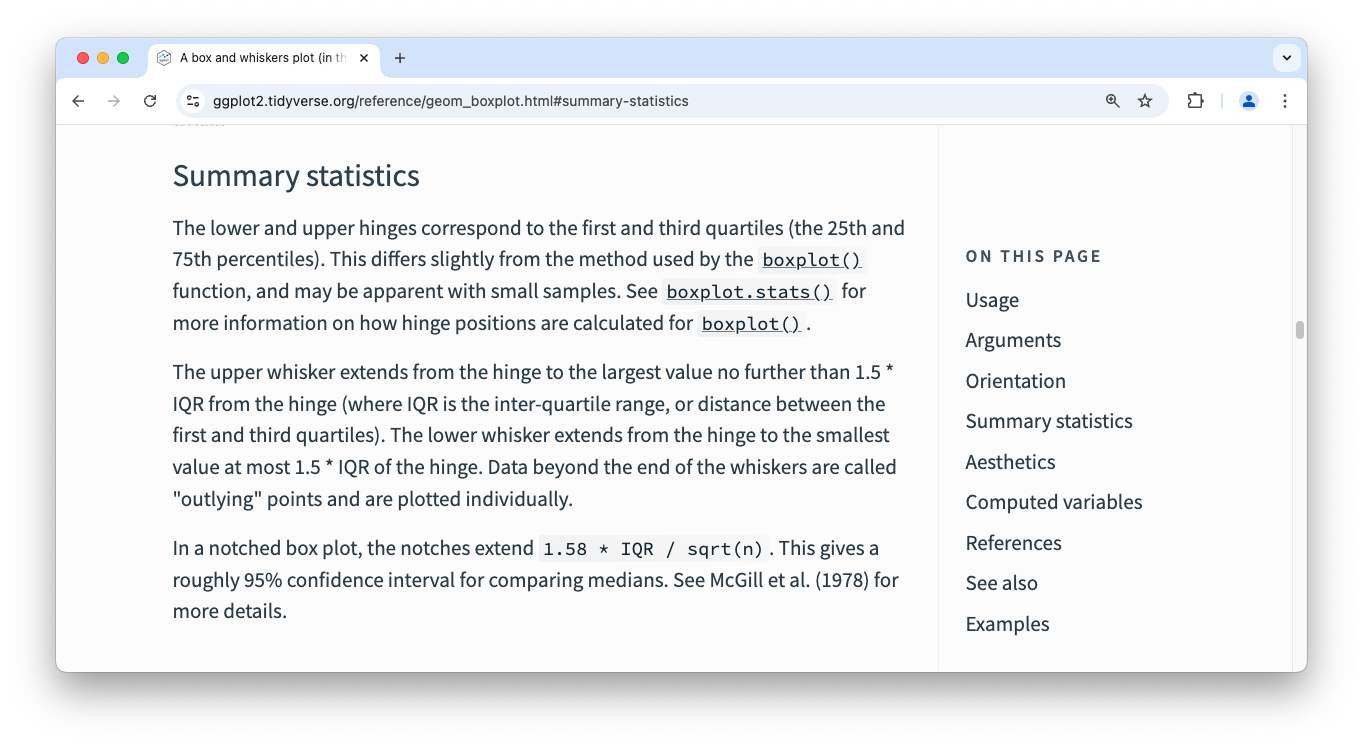
stat_boxplot()
Layering with stats
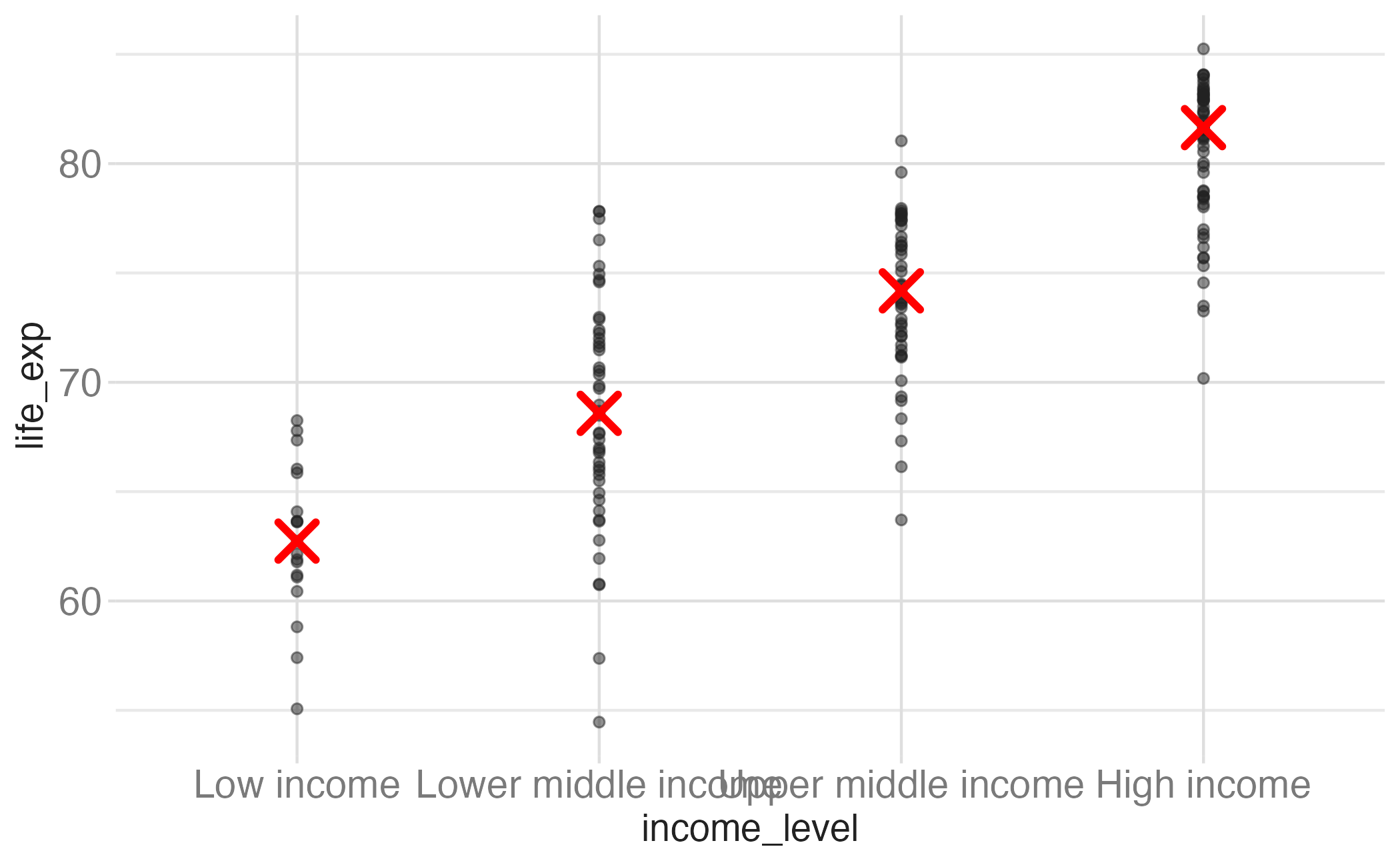
Alternate: layering with stats
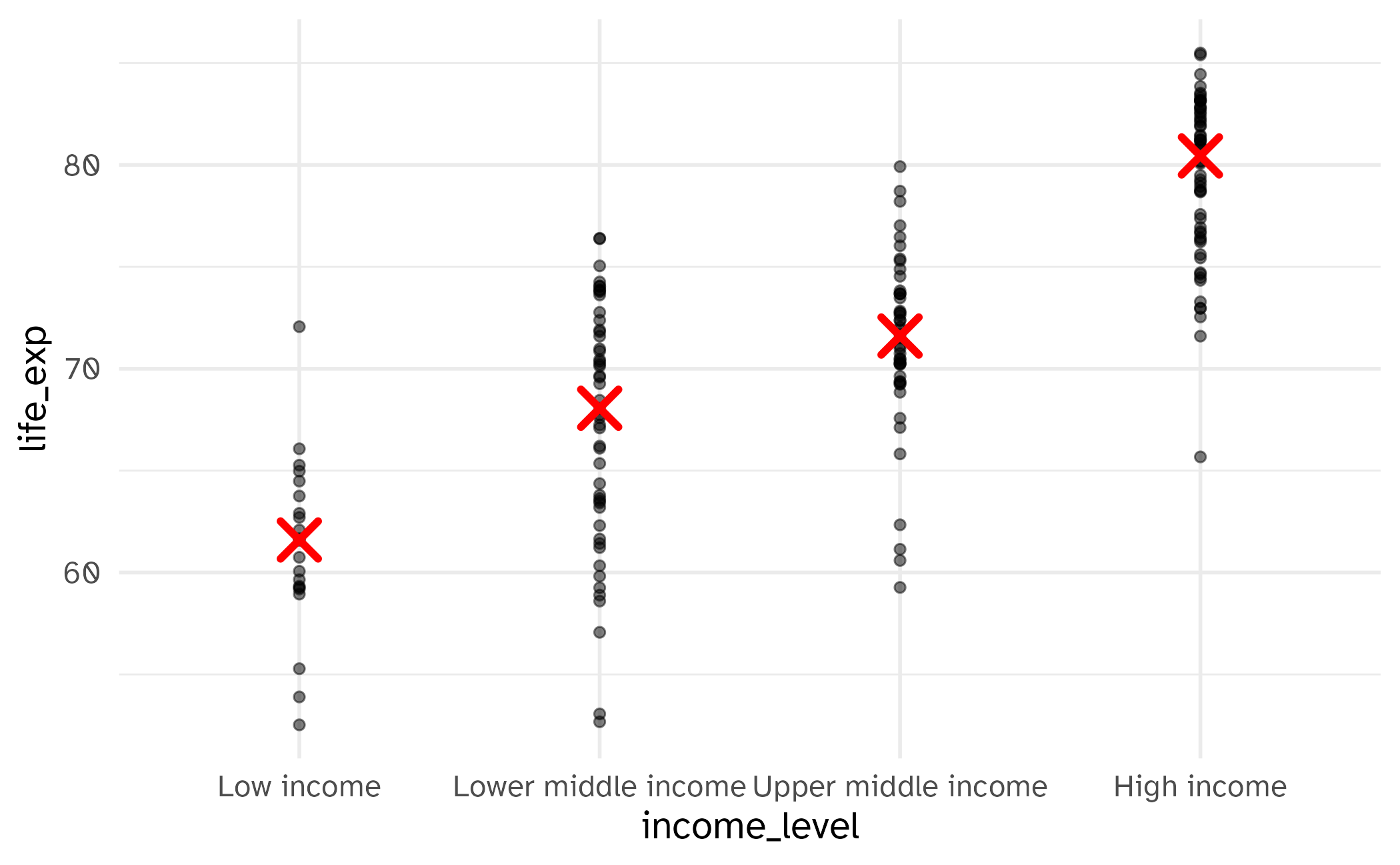
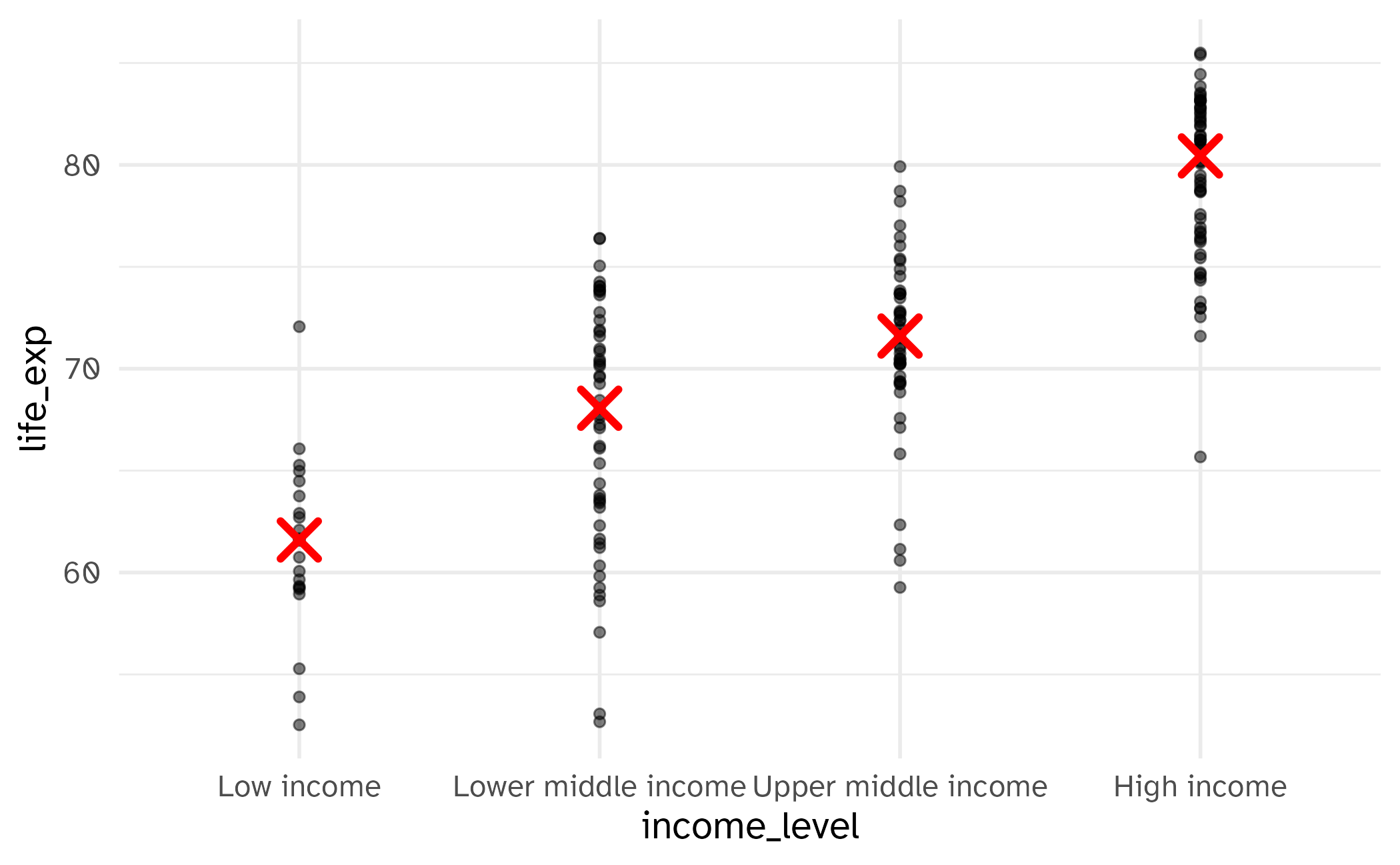
Alternate alternate: do it with {dplyr}
Scales
What is a scale?
Each scale is a function from a region in data space (the domain of the scale) to a region in aesthetic space (the range of the scale)
The axis or legend (also known as a guide) is the inverse function: it allows you to convert visual properties back to data
Scale specification
Every aesthetic in your plot is associated with exactly one scale:
Anatomy of a scale function
scale_<aes>_<type>()
- Always starts with
scale <aes>: Name of the primary aesthetic (e.g.,color,shape,x)<type>: Name of the scale (e.g.,continuous,discrete,brewer)
Guess the output
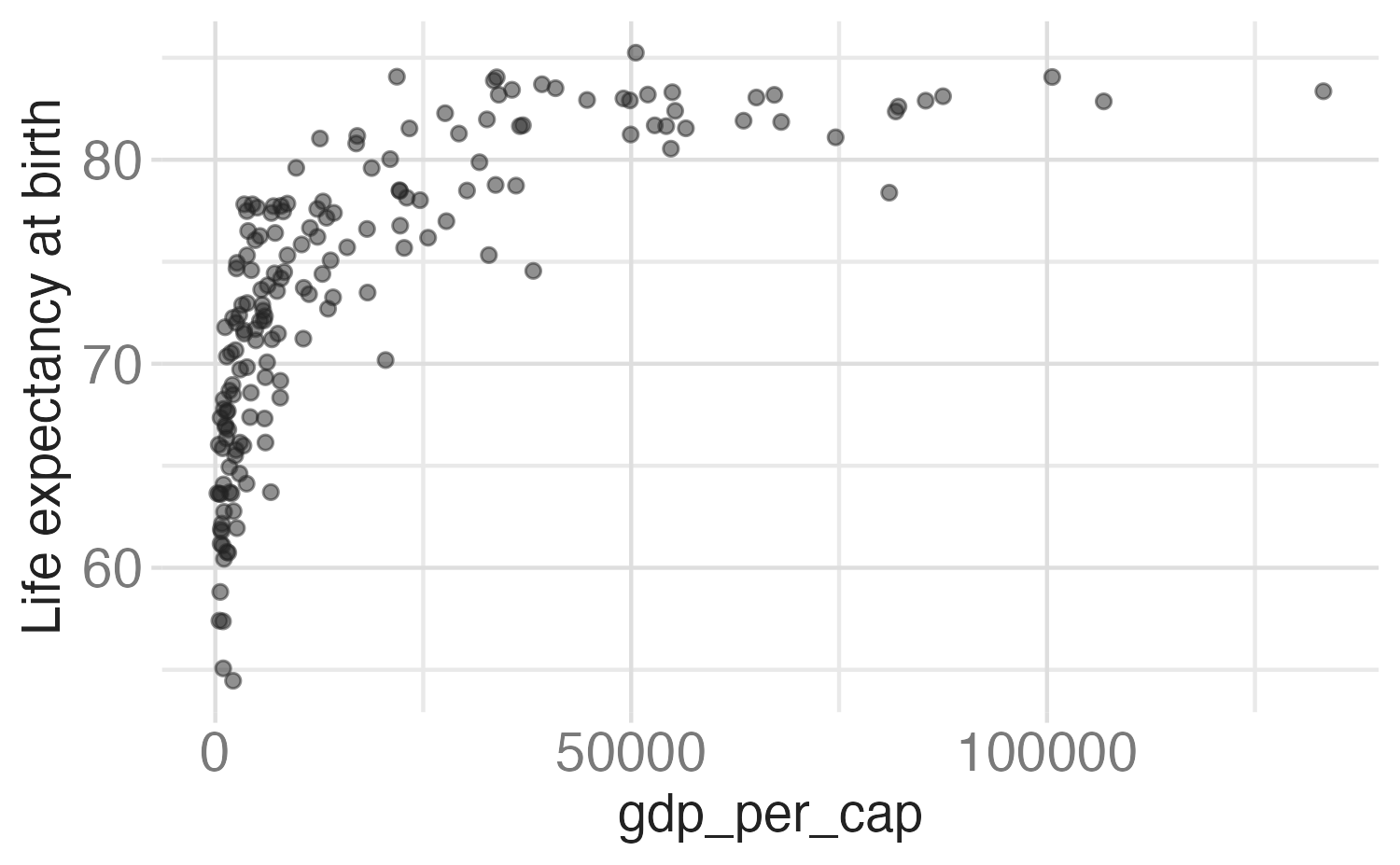
What will the x-axis label of the following plot say?
“Address” messages
Scale for x is already present.
Adding another scale for x, which will replace the existing scale.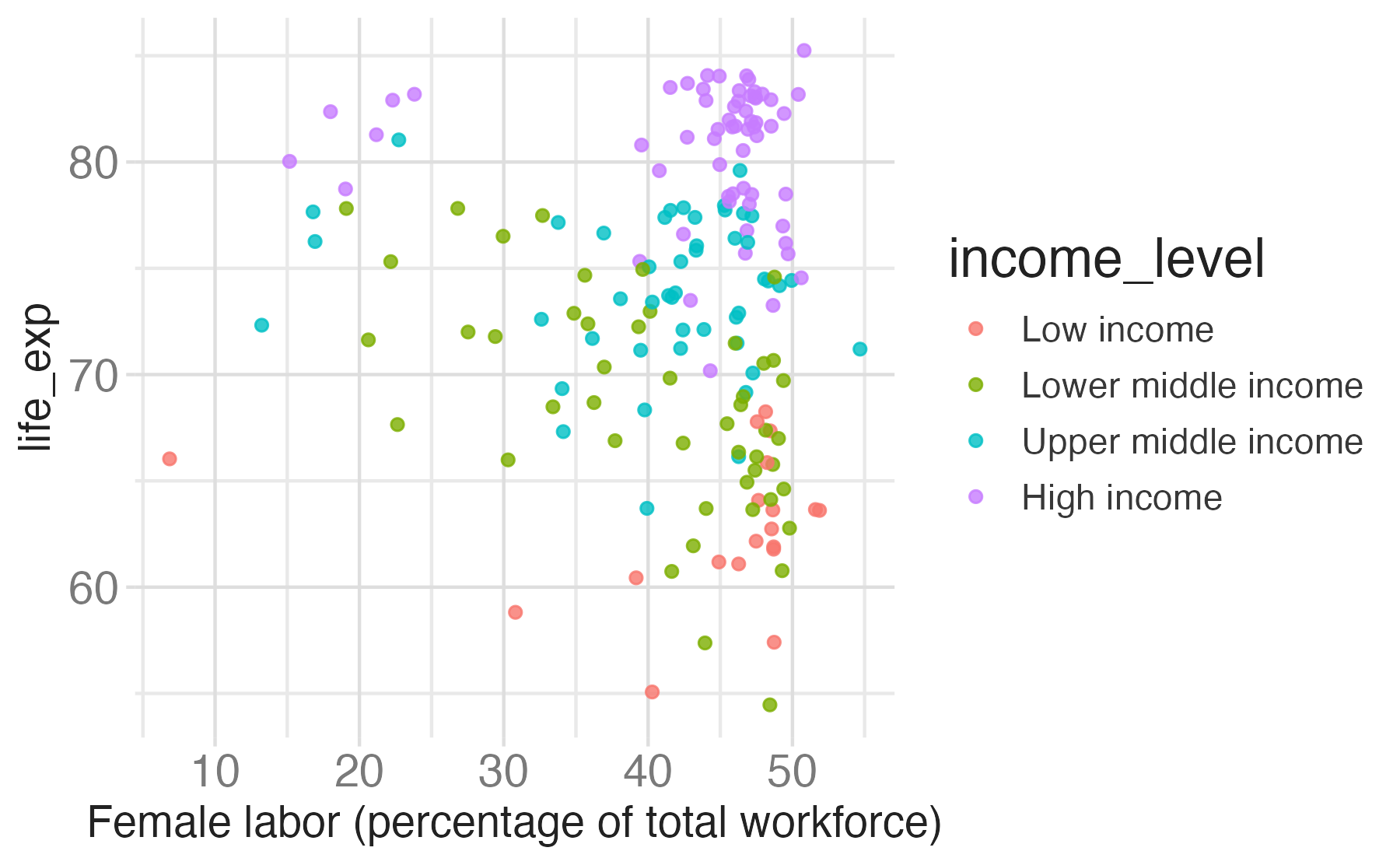
What happens if incorrect pairing?
Error in `scale_x_continuous()`:
! Discrete value supplied to a continuous scale.
ℹ Example values: Low income, Lower middle income, Upper middle income, and High income.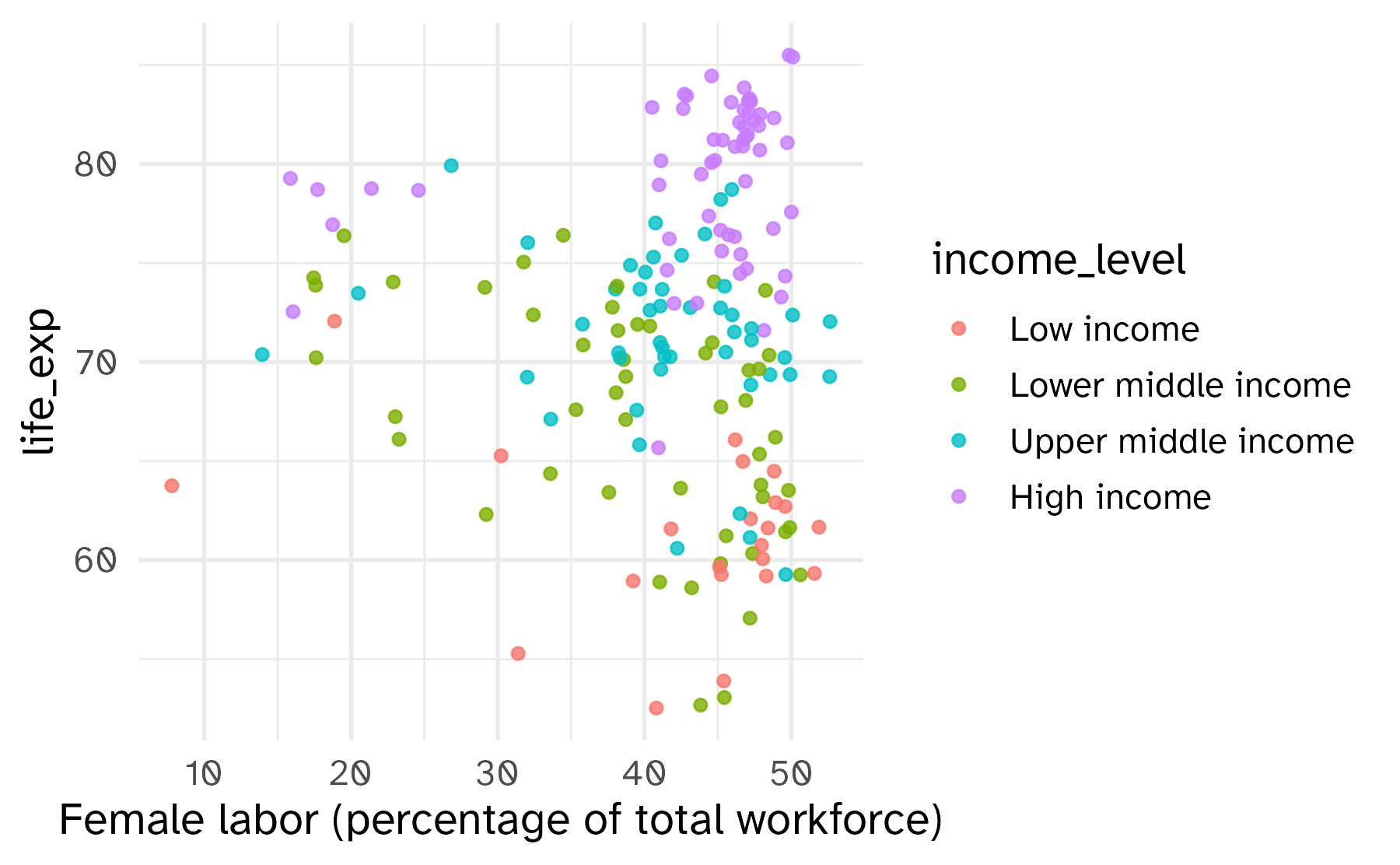
Transformations
When working with continuous data, the default is to map linearly from the data space onto the aesthetic space, but this scale can be transformed
Common scale transformations
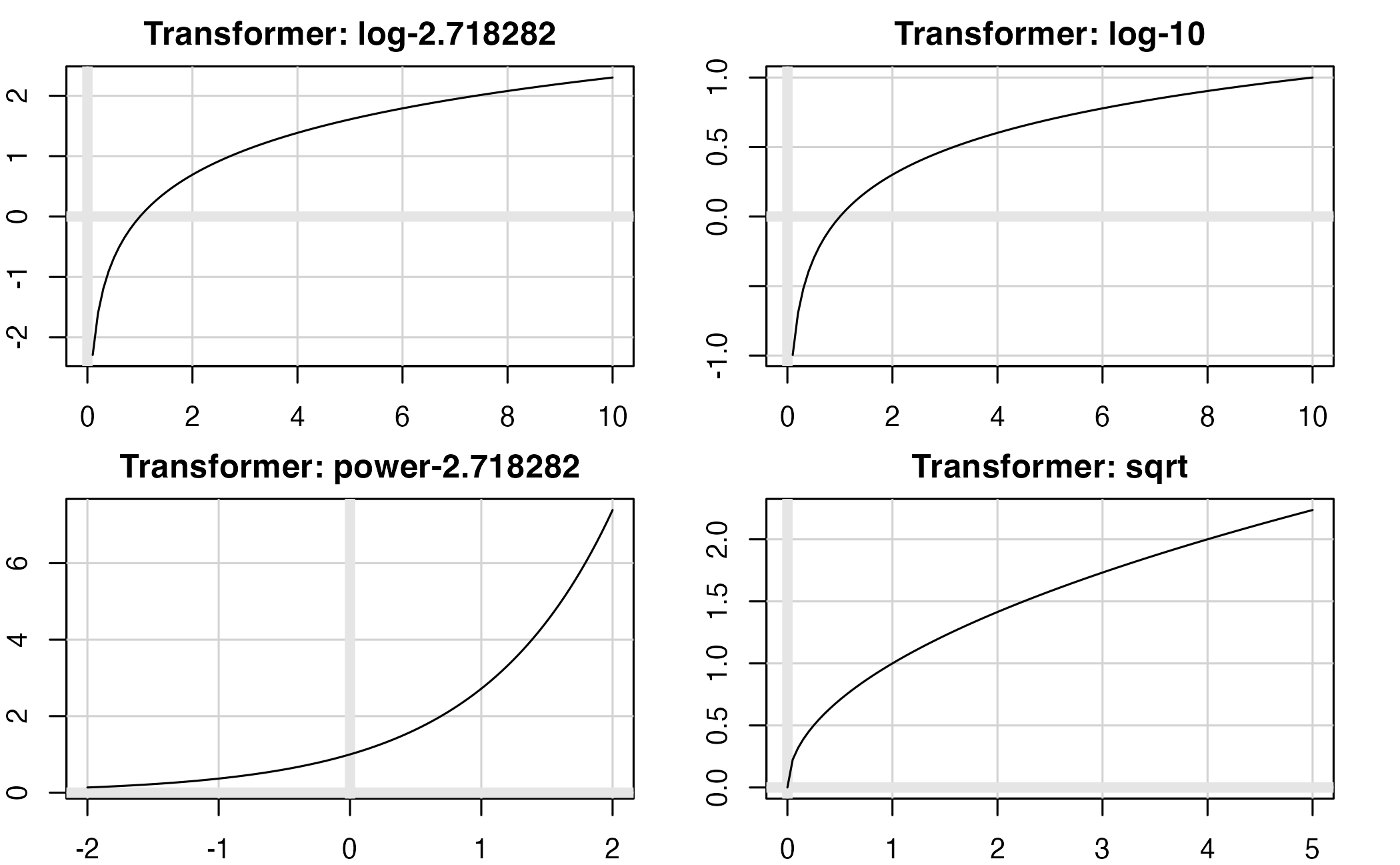
Box-Cox scale transformations
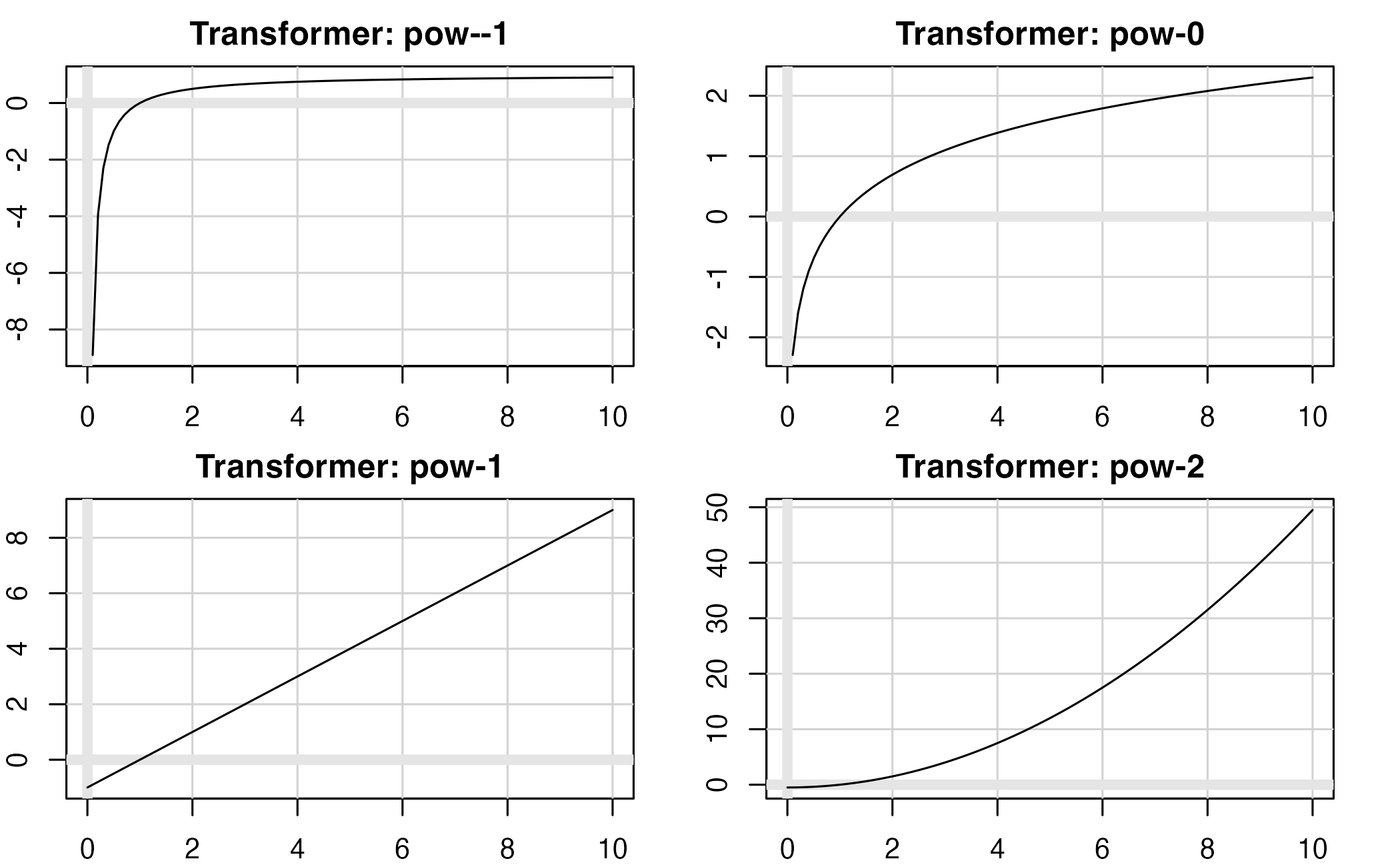
Continuous scale transformations
| Name | Function \(f(x)\) | Inverse \(f^{-1}(y)\) |
|---|---|---|
| asn | \(\tanh^{-1}(x)\) | \(\tanh(y)\) |
| exp | \(e ^ x\) | \(\log(y)\) |
| identity | \(x\) | \(y\) |
| log | \(\log(x)\) | \(e ^ y\) |
| log10 | \(\log_{10}(x)\) | \(10 ^ y\) |
| log2 | \(\log_2(x)\) | \(2 ^ y\) |
| logit | \(\log(\frac{x}{1 - x})\) | \(\frac{1}{1 + e(y)}\) |
| pow10 | \(10^x\) | \(\log_{10}(y)\) |
| probit | \(\Phi(x)\) | \(\Phi^{-1}(y)\) |
| reciprocal | \(x^{-1}\) | \(y^{-1}\) |
| reverse | \(-x\) | \(-y\) |
| sqrt | \(x^{1/2}\) | \(y ^ 2\) |
Convenience functions for transformations
Application exercise
ae-04
Instructions
- Go to the course GitHub org and find your
ae-04(repo name will be suffixed with your GitHub name). - Clone the repo in Positron, run
renv::restore()to install the required packages, open the Quarto document in the repo, and follow along and complete the exercises. - Render, commit, and push your edits by the AE deadline – end of the day
Work through part 1
Implement log transformations.
07:00
Guides
What is a guide?
Guides are axes and legends:
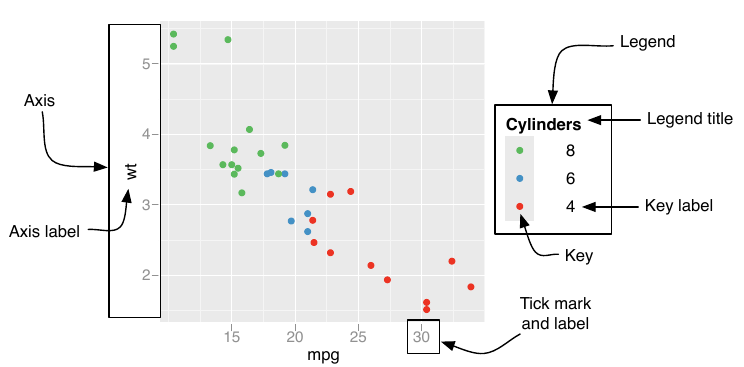
Source: ggplot2-book Chp 14.
Customizing axes
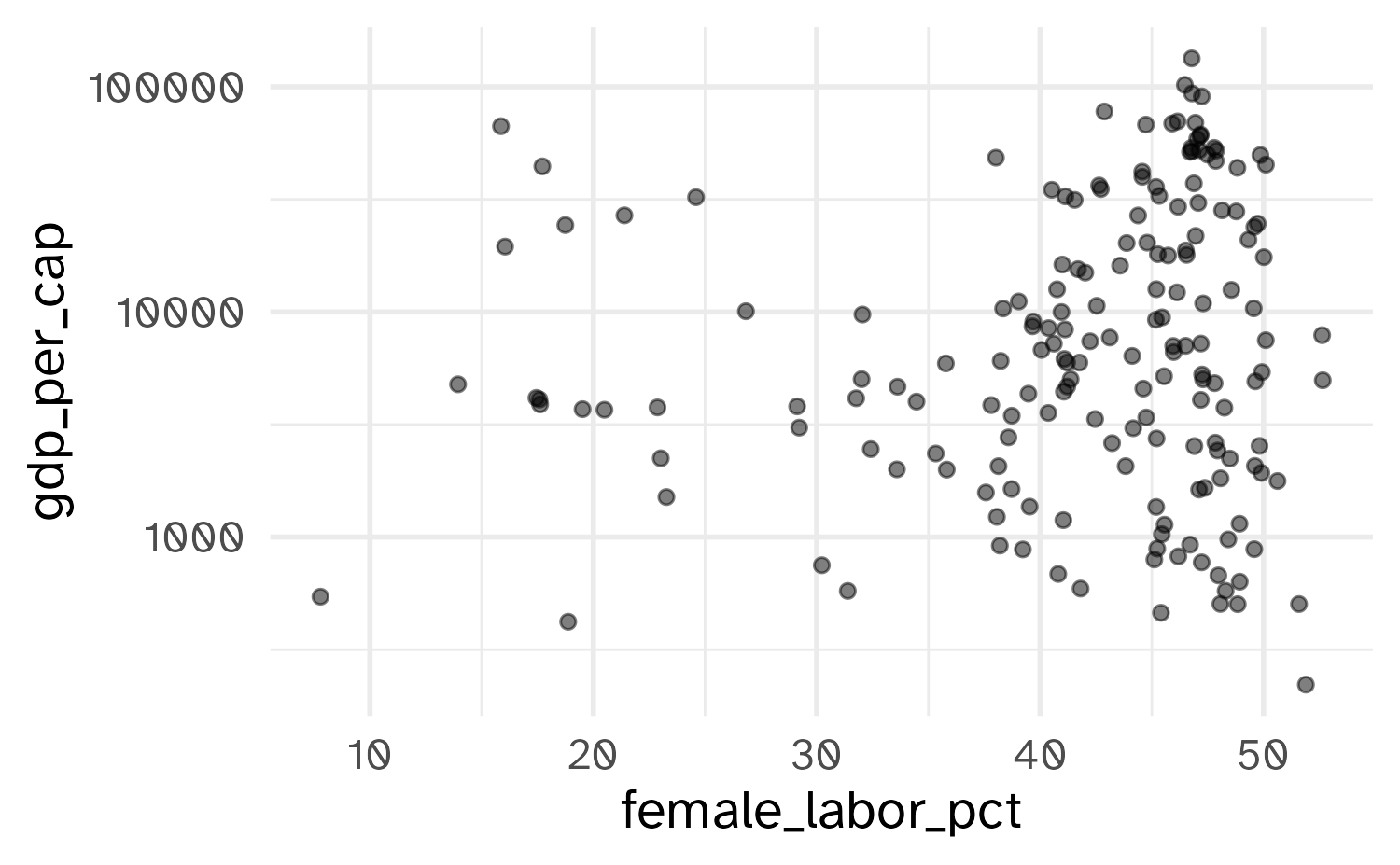
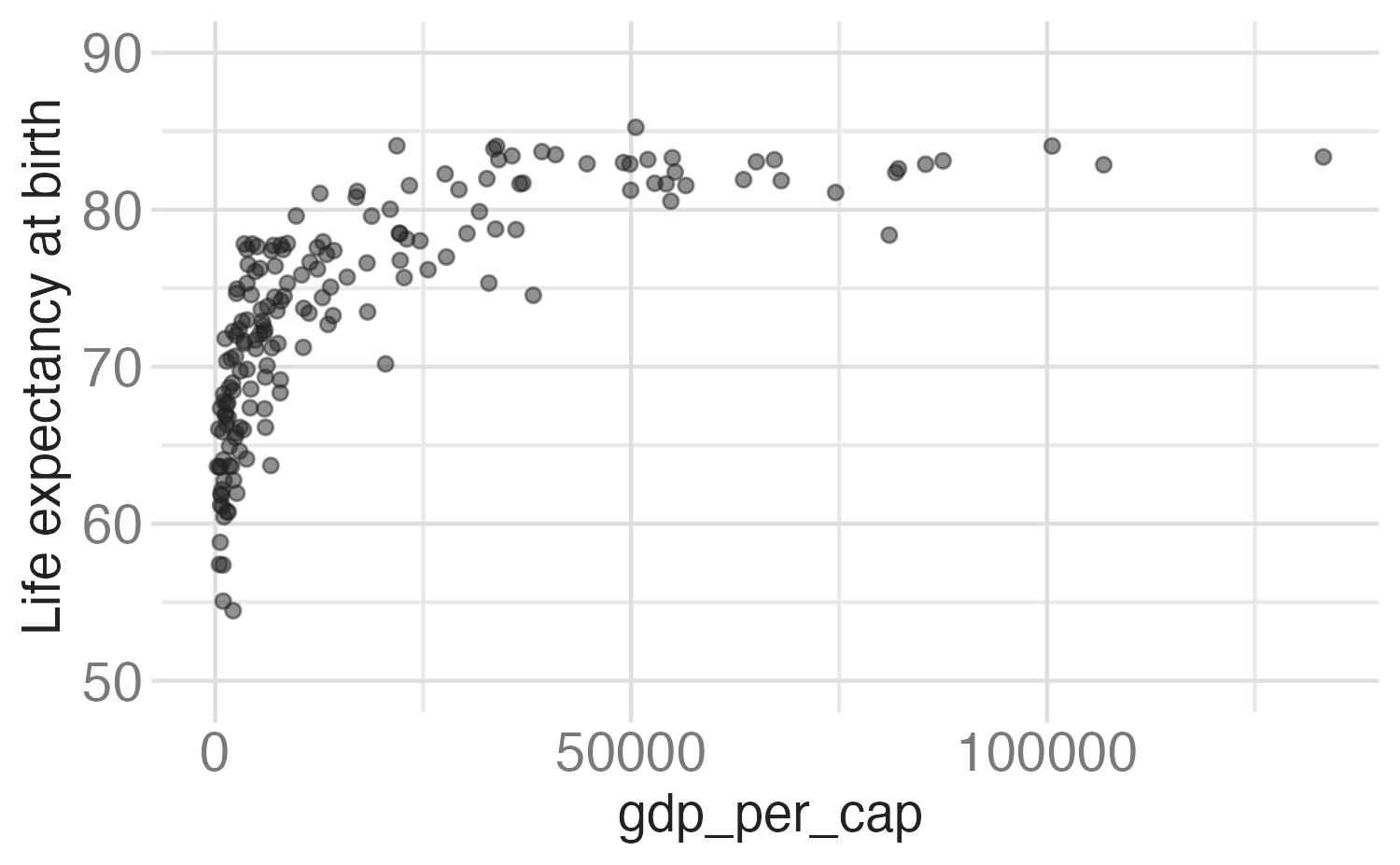
Customizing axes
Why do 50 and 90 not appear on the \(y\)-axis?
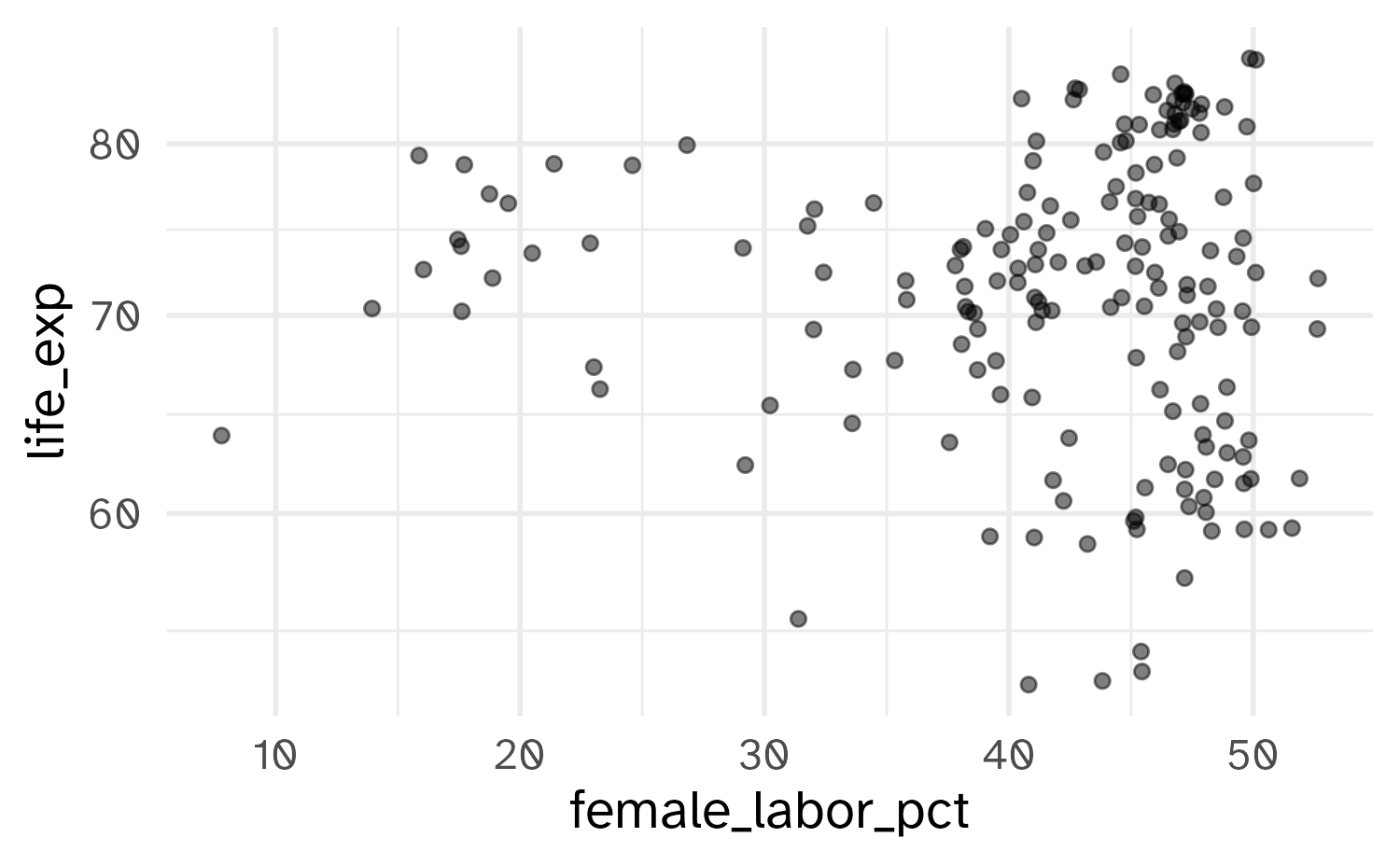
Customizing axes
Customizing axes
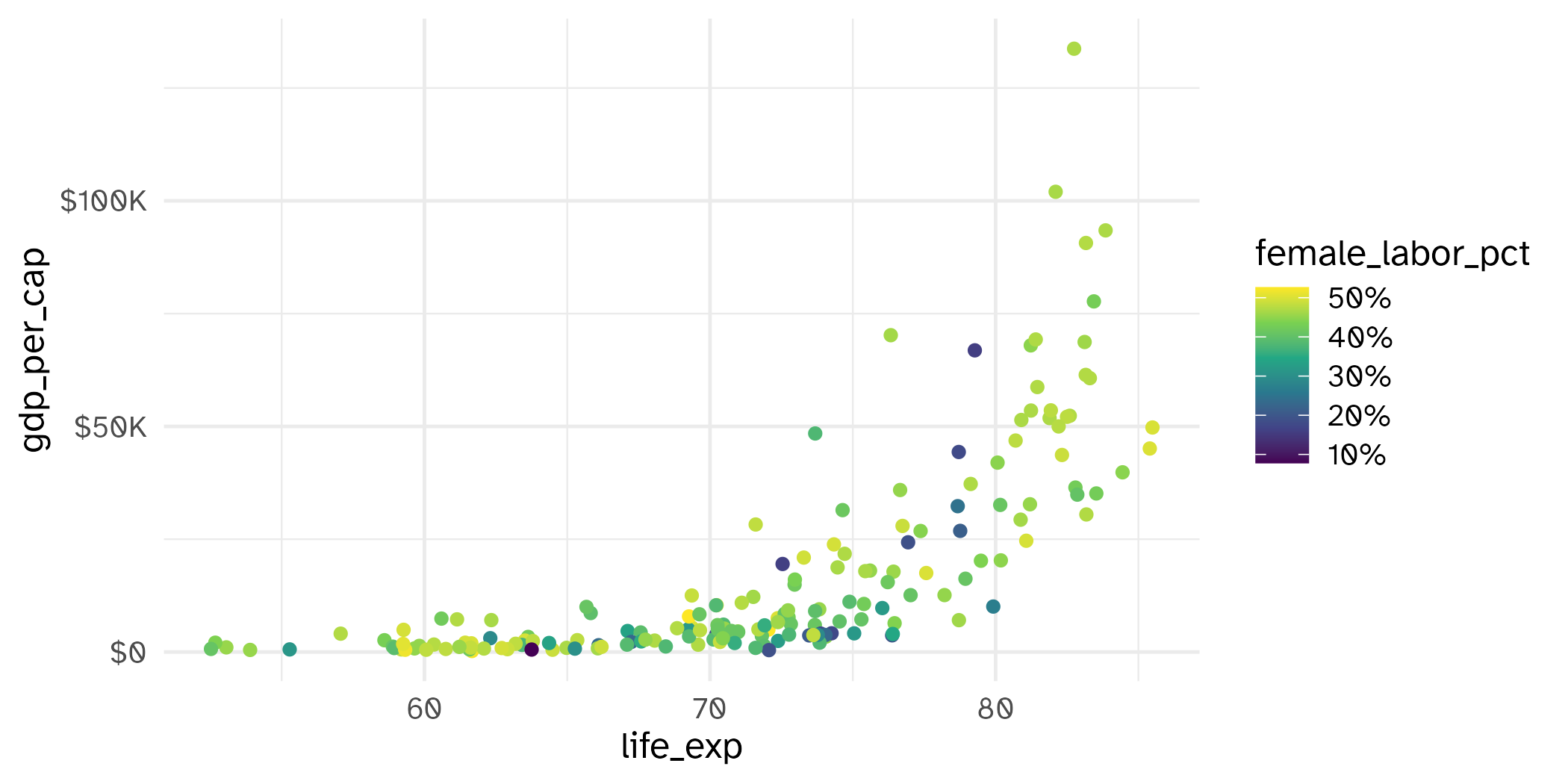
ggplot(world_bank, aes(x = gdp_per_cap, y = life_exp)) +
geom_point(alpha = 0.5) +
scale_y_continuous(
name = "Life expectancy at birth",
breaks = seq(from = 50, to = 90, by = 10),
limits = c(50, 90)
) +
scale_x_continuous(
name = "GDP per capita",
breaks = c(0, 5e04, 1e05),
labels = c("$0", "$50,000", "$100,000")
)
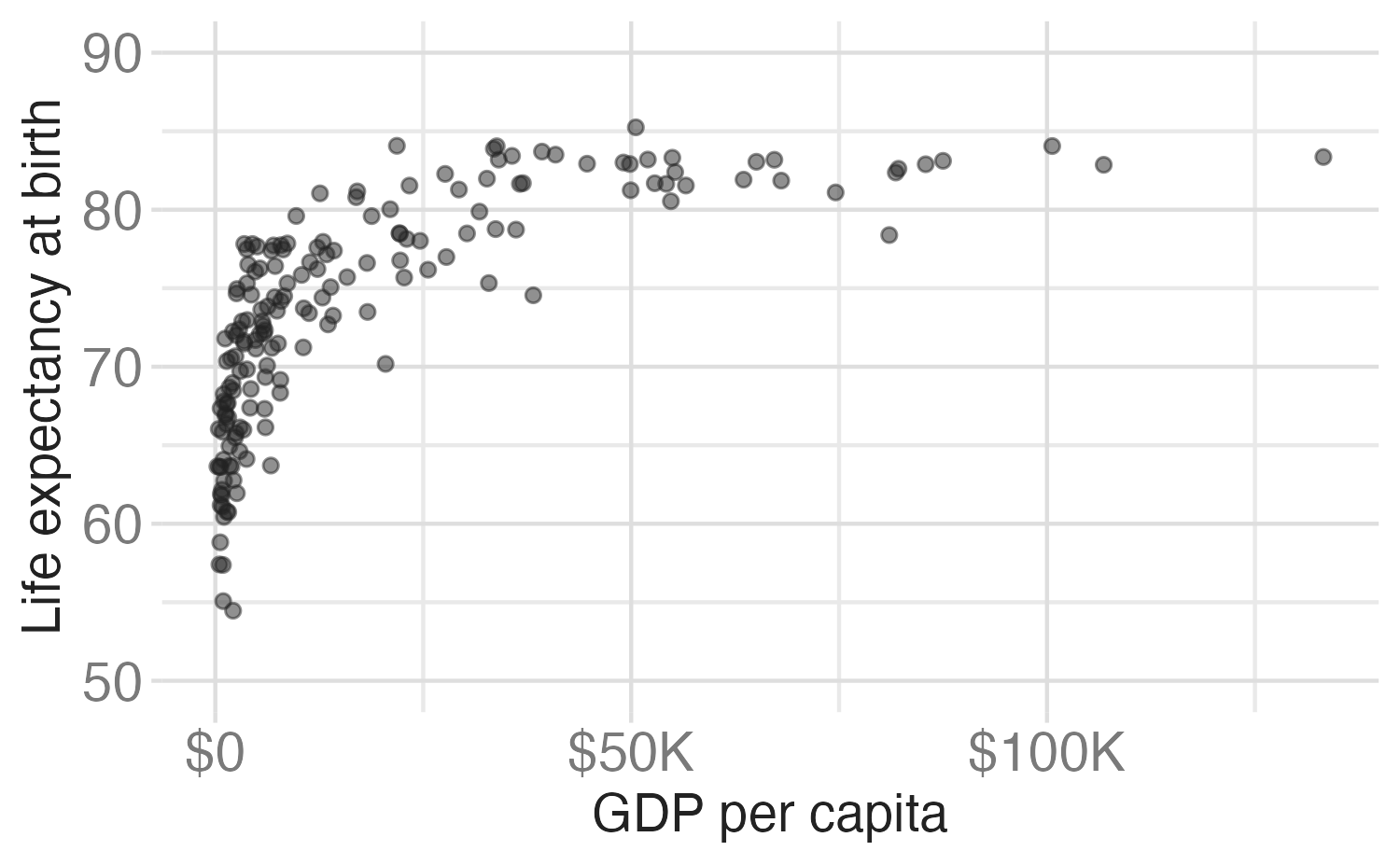
Customizing axes
Customizing axes
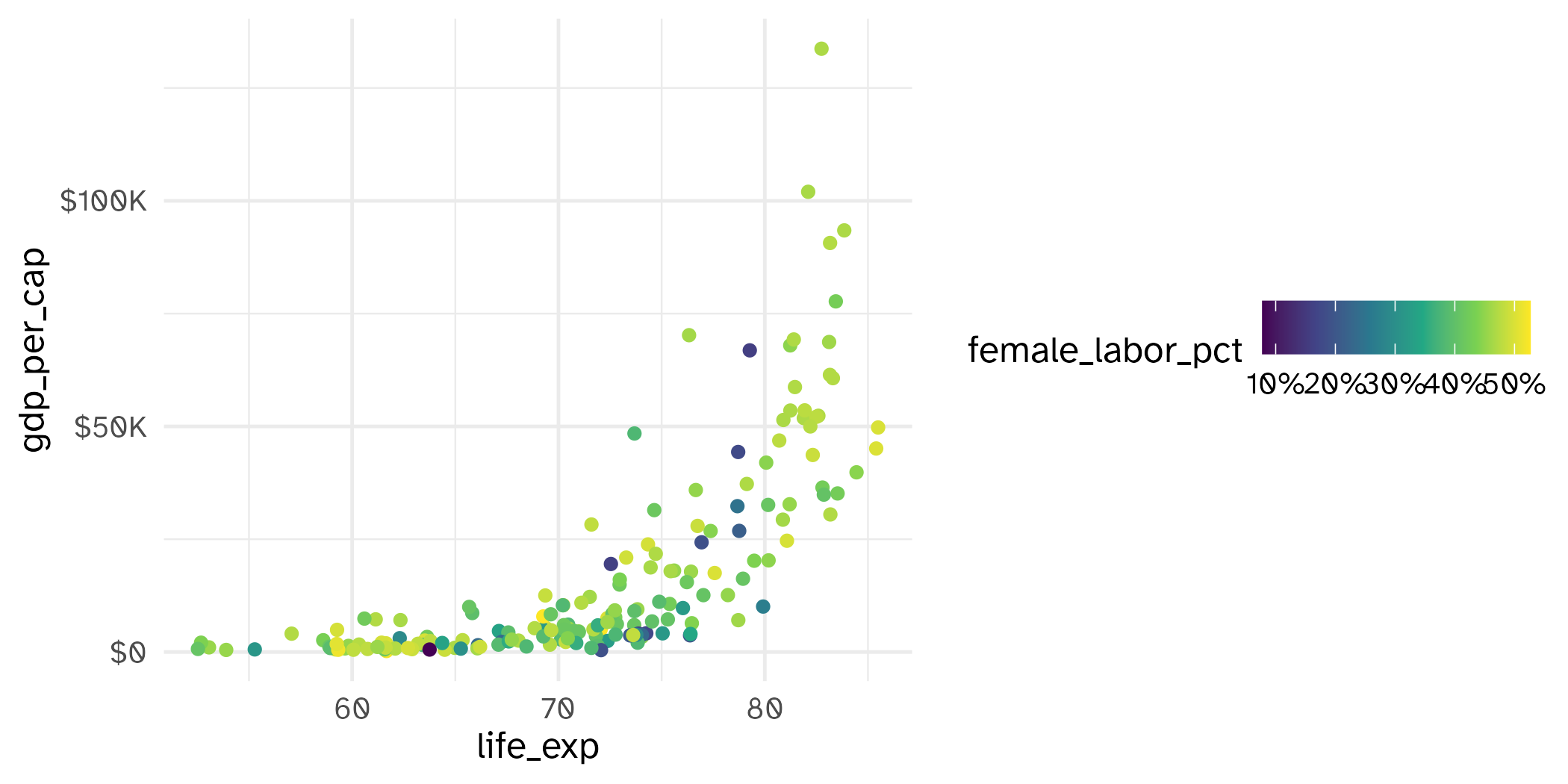
ggplot(world_bank, aes(x = gdp_per_cap, y = life_exp)) +
geom_point(alpha = 0.5) +
scale_y_continuous(
name = "Life expectancy at birth",
breaks = seq(from = 50, to = 90, by = 10),
limits = c(50, 90)
) +
scale_x_continuous(
name = "GDP per capita",
labels = label_currency(scale_cut = cut_short_scale())
)
Modifying scale guides
Scale guides
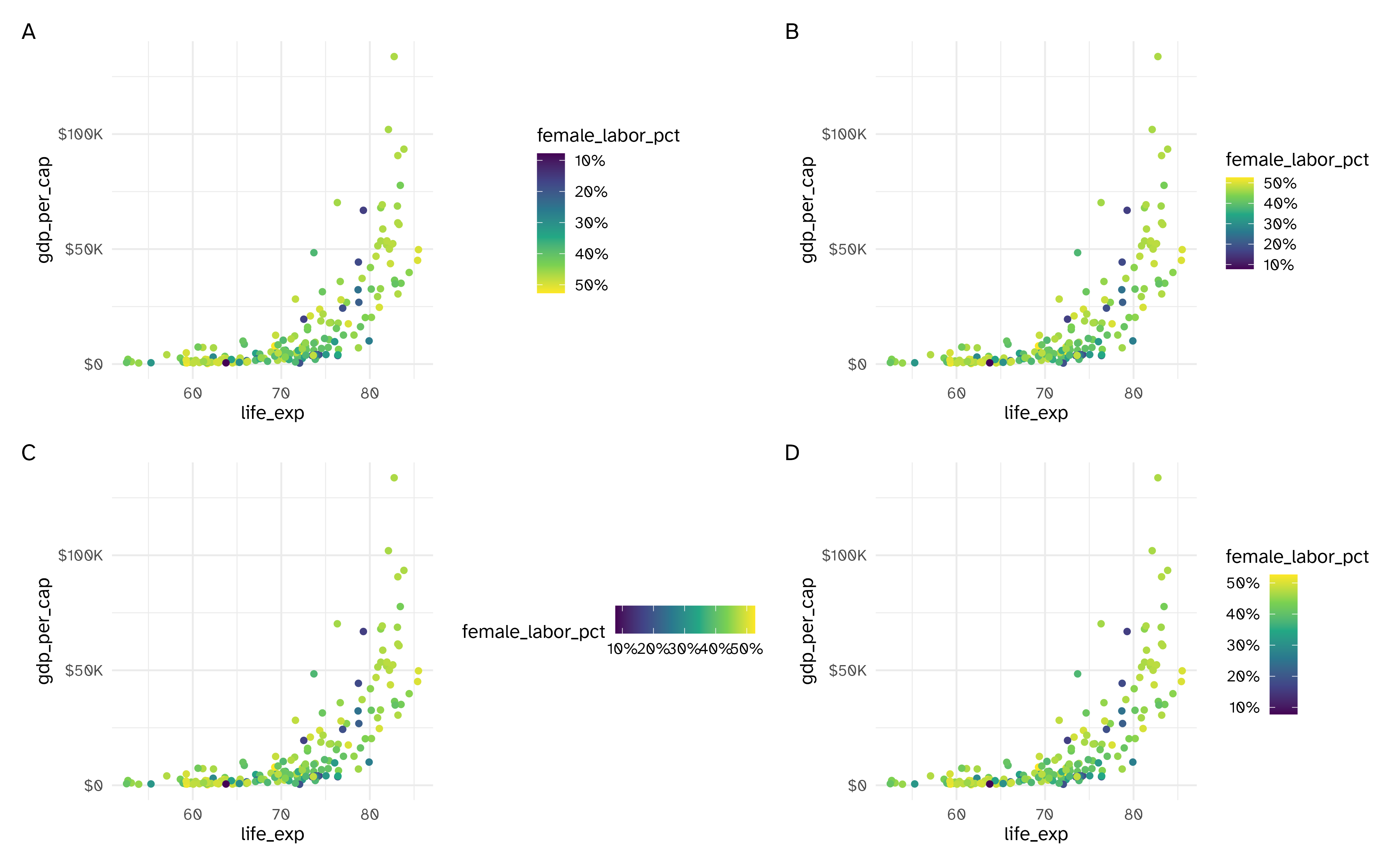
Scale guides
| Scale type | Default guide type | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Continuous scales for color/fill aesthetics | colorbar | guide_colorbar() |
| Binned scales for color/fill aesthetics | colorsteps | guide_colorsteps() |
| Position scales (continuous, binned and discrete) | axis | guide_axis() |
| Discrete scales (except position scales) | legend | guide_legend() |
| Binned scales (except position/color/fill scales) | bins | guide_bins() |
Implementation
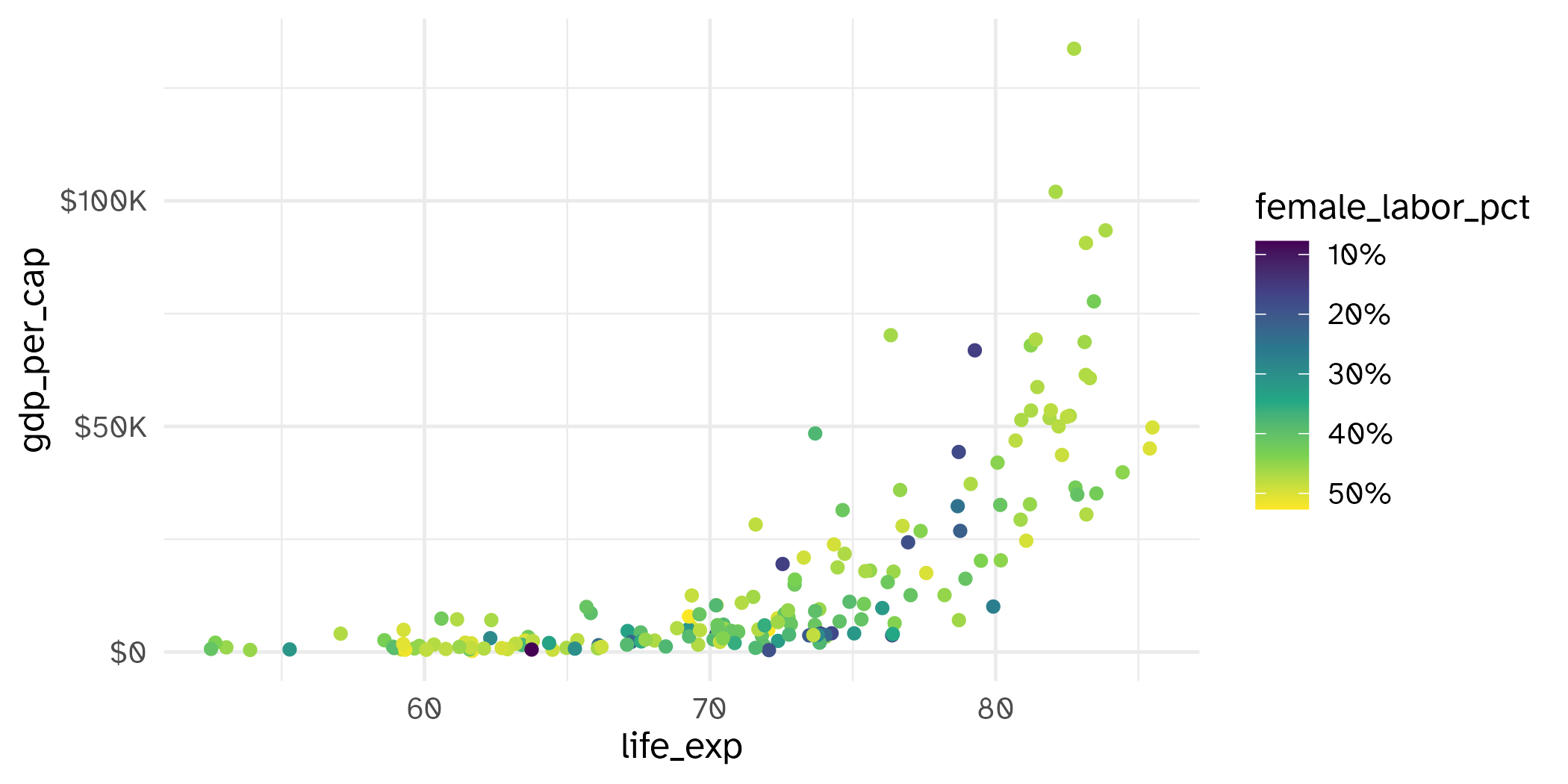
Example implementation
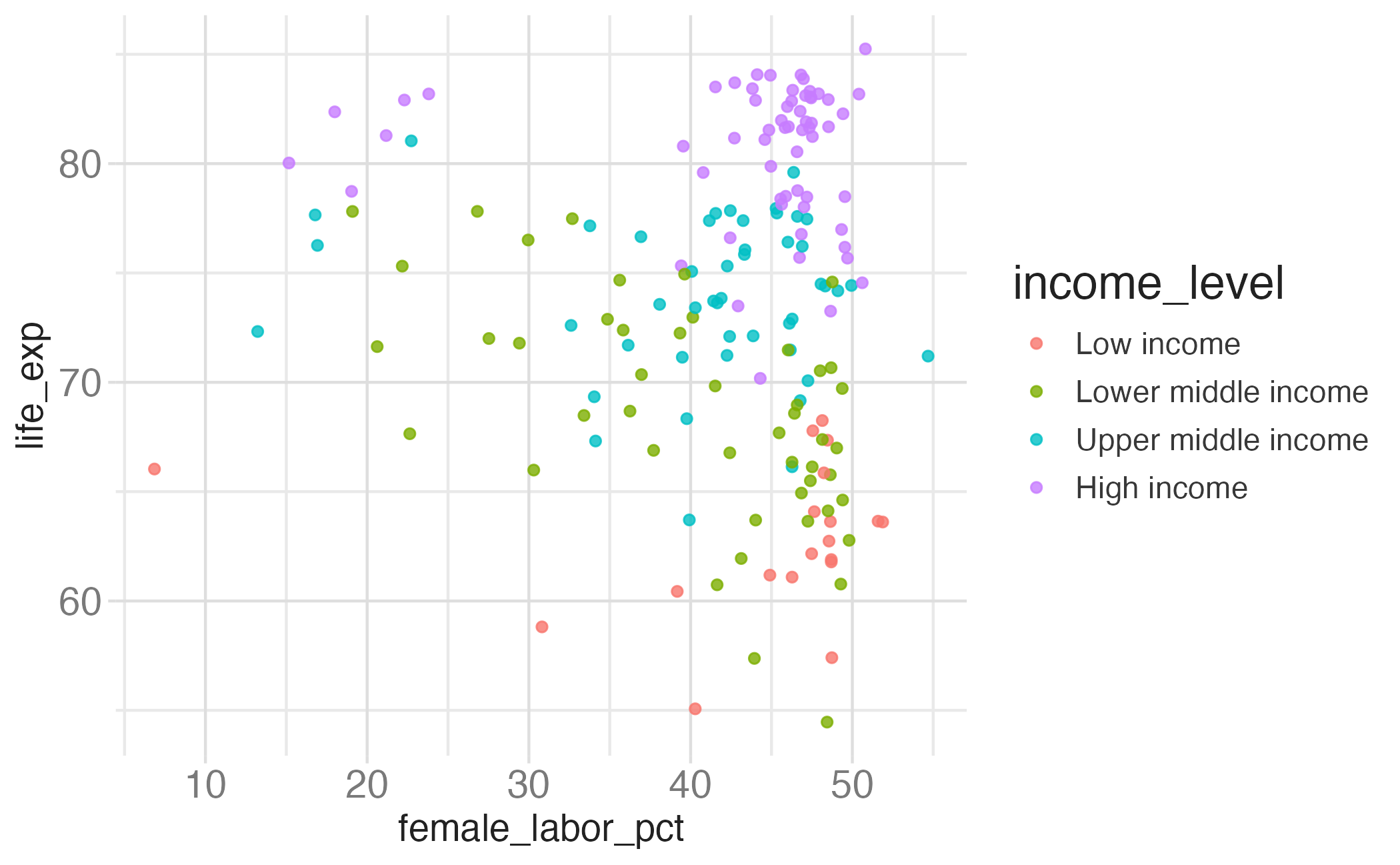
Application exercise
ae-04
Work through part 2
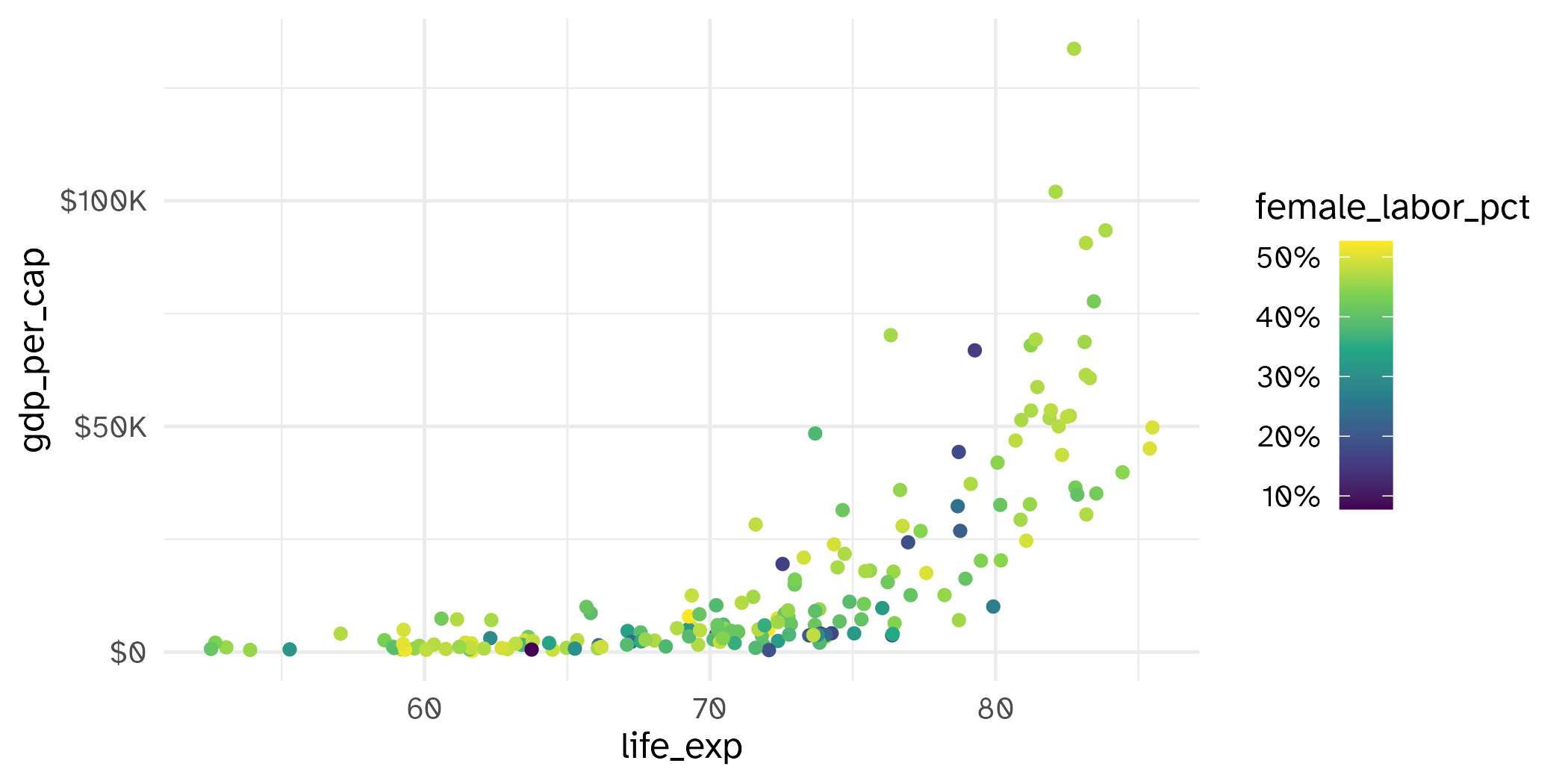
Recreate this plot.
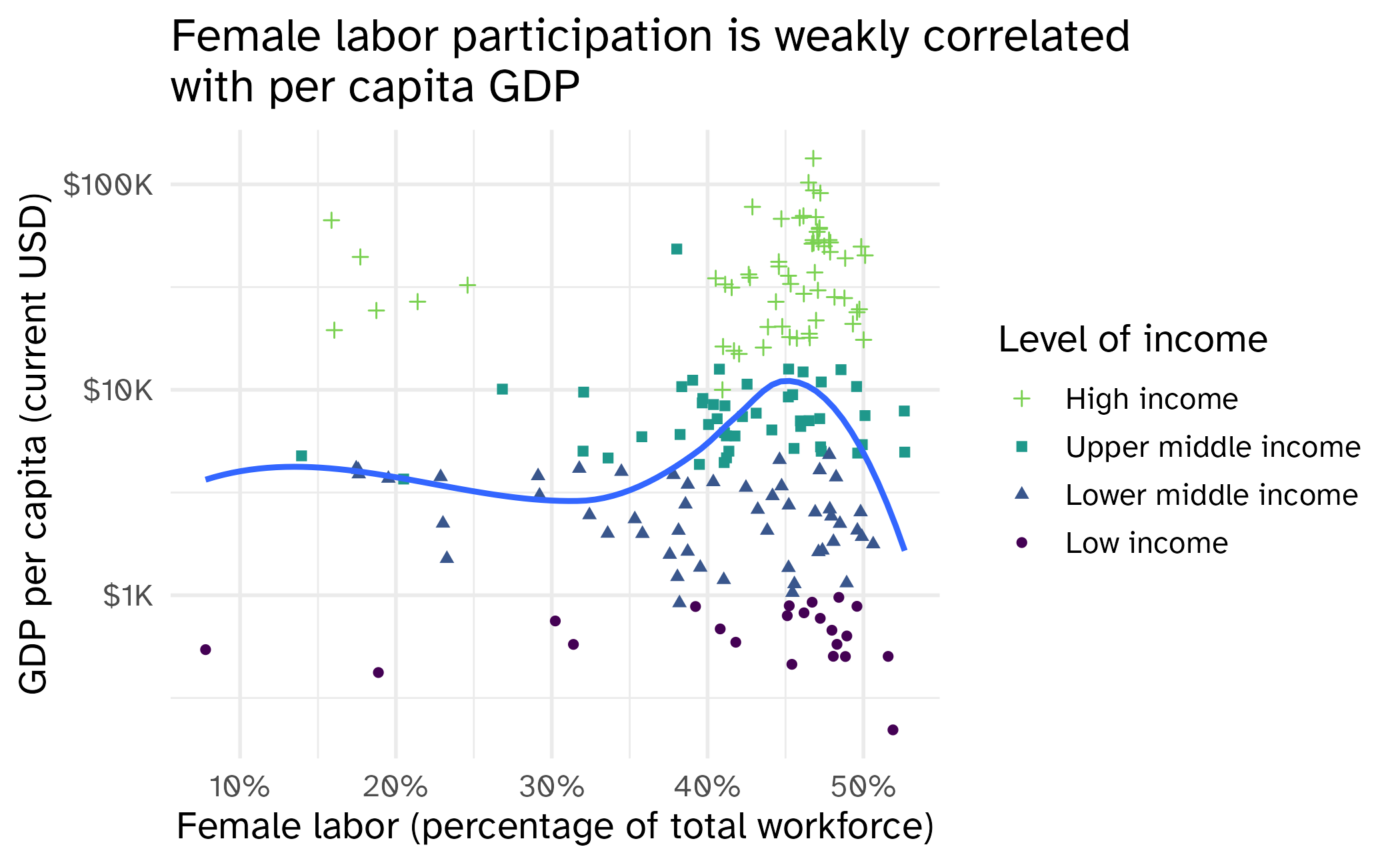
10:00
Wrap up
Recap
- {ggplot2} implements statistical transformations (typically as defaults)
- Scales visually encode data to mappings
- Guides control the appearance of scales
- {scales} package provides a wide range of transformation and formatting functions
- Use
guide_*()functions to customize the appearance of guides
Acknowledgements
- Slides derived in part from STA 313: Advanced Data Visualization